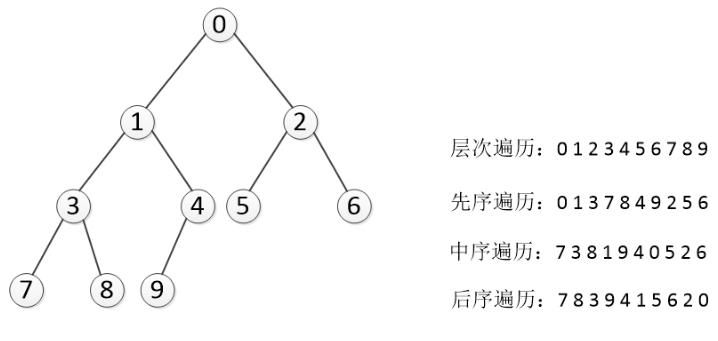
7.二叉树的遍历
树的遍历是书的一种重要的运算,所谓遍历是指对树中所有节点的信息的访问,即一次对树中每个节点访问一次且仅访问一次,我们把这种对所有节点的访问称为遍历(traveral)。那么树的两种重要的遍历模式是深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历,深度优先一般用递归,广度优先一般用队列,一般情况下能用递归实现的算法大部分也能用堆栈来实现。
深度优先遍历
对于一颗二叉树,深度优先搜素(Depth First Search)是沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。
那么深度遍历有重要的三种方法。这三种方式常被用于访问树的节点,他们之间的不同在于访问每个节点的次序不同。这三种遍历分别叫做先序遍历(preorder),中序遍历(inorder),和后序遍历(prstorder)。我们给出详细定义,然后举例看看它们的应用。
先序遍历
在先序遍历中,我们先访问根节点,然后递归使用先序遍历访问左子树,然后再递归使用先序遍历访问右子树。
访问的顺序为:根节点->左子树->右子树
代码实现
1 | class Tree(object): |
中序遍历
在中序遍历中,我们递归使用中序遍历访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后再递归使用中序遍历访问右子树
访问顺序为:左子树->根节点->右子树
代码实现
1 | class Tree(object): |
后续遍历
在后续遍历中,我们先递归使用后序遍历访问左子树和右子树,最后访问根节点。
访问顺序为:左子树->右子树->根节点
代码实现
1 | class Tree(object): |
广度优先遍历(层次遍历)
从树的root开始,从上到下从左到右遍历整个树的节点
代码实现
1 | class Tree(object): |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 咋的个人博客!